Table of Contents
Introduction to Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic management tool that has gained significant recognition and adoption in various industries. It provides organizations with a comprehensive framework to assess and improve their performance by considering multiple perspectives, beyond just financial measures. The Balanced Scorecard allows businesses to align their strategic objectives, measure progress, and drive positive outcomes across different facets of their operations. It has become an invaluable tool for managers to gain a holistic view of their organizations and enhance decision-making processes.
Quality Glossary Definition
The Balanced Scorecard can be defined as a management system that provides feedback on both internal business processes and external outcomes to continuously improve strategic performance and results. It goes beyond traditional financial measures and considers four key perspectives: financial, customer, business process, and learning and growth. By incorporating these perspectives, organizations can evaluate their performance across various dimensions and identify areas for improvement.
Balanced Scorecard as a Strategic Management Tool & Historical Context
Originally developed by Robert Kaplan, a professor at Harvard Business School, and David Norton, a business executive and consultant, the Balanced Scorecard emerged in the early 1990s as a response to the limitations of relying solely on financial indicators. Kaplan and Norton recognized that financial measures alone did not provide a comprehensive assessment of an organization’s health and future prospects.
They argued that organizations needed to consider a broader range of factors to evaluate their performance and guide strategic decision-making. They introduced the concept of the Balanced Scorecard in their seminal book, “The Balanced Scorecard: Translating Strategy Into Action,” which emphasized the importance of integrating financial and non-financial measures to better align strategic objectives with performance evaluation.
Since its inception, the Balanced Scorecard has evolved into a widely adopted strategic management tool. It has been successfully implemented by organizations of all sizes and across various sectors, including for-profit companies, nonprofit organizations, and government agencies. Its versatility and effectiveness lie in its ability to translate abstract strategy into actionable goals and performance measures, facilitating better communication, coordination, and organizational alignment.
The Balanced Scorecard has played a transformative role in helping organizations navigate the complexities of modern business environments. By incorporating a balanced set of measures and perspectives, it enables a more comprehensive assessment of performance and fosters continuous improvement. Its impact and success have solidified its position as a vital tool for strategic management.
Detailed Examination of the Four Perspectives of Balanced Scorecard
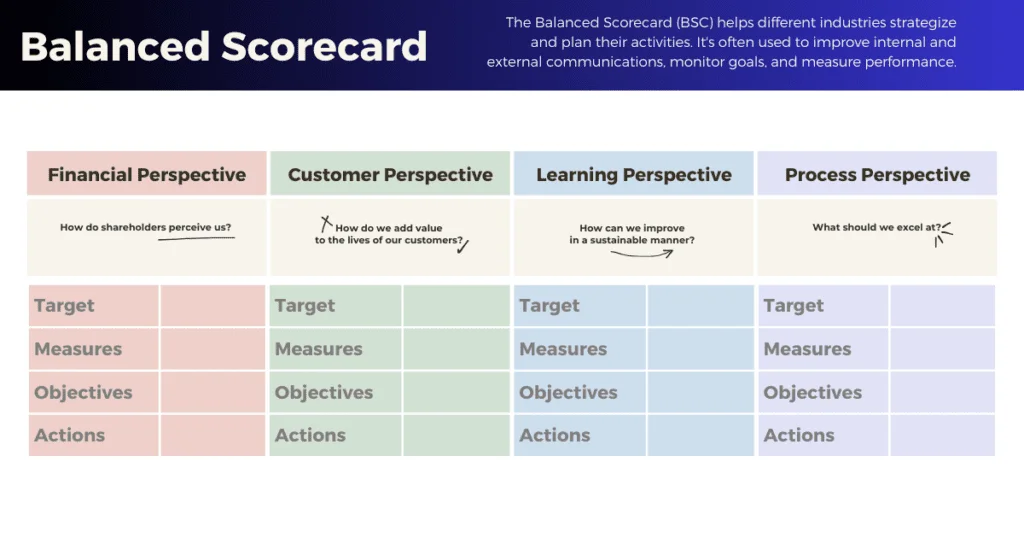
The Balanced Scorecard framework consists of four key perspectives that provide a comprehensive view of an organization’s performance. Each perspective represents a different dimension of the organization’s operations and offers valuable insights into specific areas that contribute to overall success. These perspectives are the financial perspective, customer perspective, internal process perspective, and learning and growth perspective.
1. Financial Perspective:
The financial perspective focuses on evaluating the organization’s financial health and performance. Key metrics under this perspective include revenue growth, profitability, return on investment, cash flow, and cost efficiency. By assessing financial indicators, organizations gain insights into their ability to generate value for stakeholders and achieve sustainable financial success.
2. Customer Perspective:
The customer perspective revolves around understanding and meeting the needs of the organization’s customers. It involves assessing customer satisfaction, loyalty, retention, and acquisition. Key performance indicators (KPIs) under this perspective encompass metrics such as customer satisfaction scores, customer lifetime value, market share, and customer acquisition rates. By considering the customer perspective, organizations can align their strategies to deliver superior value and experiences to their customers.
Enrol in: Voice of the Customer Toolkit Certification Course
3. Internal Process Perspective:
The internal process perspective centers on evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of the organization’s internal processes. It involves identifying and measuring the key processes that drive the delivery of products or services to customers. KPIs in this perspective can include metrics related to operational efficiency, quality, cycle time, and productivity. By focusing on internal processes, organizations can identify areas for improvement and enhance their overall operational performance.
4. Learning and Growth Perspective:
The learning and growth perspective emphasizes an organization’s efforts to develop and improve its human capital, systems, and culture. It encompasses employee training and development, knowledge management, innovation, and organizational capacity building. KPIs under this perspective may include metrics related to employee satisfaction, training hours, employee turnover rates, and the implementation of new technologies. By investing in learning and growth, organizations can foster a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability.
Strategic Objectives and KPIs:
Within each perspective of the Balanced Scorecard, organizations set specific strategic objectives that align with their overall strategy. These objectives define what the organization aims to achieve within each perspective. To effectively measure progress towards these objectives, organizations identify and track KPIs. KPIs provide tangible and measurable metrics that indicate whether strategic objectives are being met or if corrective actions are necessary. By setting clear strategic objectives and selecting relevant KPIs, organizations can monitor their progress and make informed decisions to drive performance improvement.
Through a detailed examination of the four perspectives and the establishment of strategic objectives and KPIs, organizations can effectively measure and manage their performance holistically. The Balanced Scorecard ensures that organizations consider multiple dimensions and align their actions with strategic priorities to drive success in financial, customer-centric, internal process, and learning and growth areas.
Benefits of a Balanced Scorecard

The Balanced Scorecard offers several benefits to organizations that adopt it as a strategic management tool. By providing a holistic view of performance and aligning objectives across various perspectives, the Balanced Scorecard facilitates effective communication, enhances organizational alignment, and enables regular reviews that drive continuous improvement.
1. Communication and Alignment:
One of the key benefits of the Balanced Scorecard is its ability to facilitate effective communication and alignment within an organization. By translating the organization’s vision, strategy, and objectives into tangible measures and targets, the Balanced Scorecard creates a shared language and understanding among employees at all levels. It ensures that everyone is working toward common goals and promotes alignment between different departments and functions. This alignment helps break down silos, fosters collaboration, and promotes a more cohesive and focused approach to achieving organizational objectives.
2. Regular Reviews and Organizational Alignment:
The Balanced Scorecard promotes regular reviews and performance evaluations across the organization. This ongoing monitoring allows managers to track progress, identify performance gaps, and take corrective actions in a timely manner. By regularly reviewing performance against established measures and targets, organizations can ensure that they stay on track and make necessary adjustments to achieve strategic objectives. It also enables proactive decision-making based on current and accurate performance data. Regular reviews foster a culture of accountability, continuous improvement, and organizational learning.
Overall, the Balanced Scorecard offers organizations a powerful framework to enhance communication, alignment, and performance management. By combining financial and non-financial measures, it enables organizations to assess their performance comprehensively, identify areas for improvement, and align actions with strategic objectives. The benefits of the Balanced Scorecard extend beyond measurement, fostering a culture of transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement throughout the organization.
Balanced Scorecard Resources

Implementing a Balanced Scorecard requires effective strategies and measures, along with a focus on driving alignment and utilizing performance indicators. These resources play a crucial role in successfully utilizing the Balanced Scorecard framework to improve organizational performance and achieve strategic goals.
1. Strategies and Measures:
To effectively implement a Balanced Scorecard, organizations need to develop clear strategies and measures that align with their objectives and desired outcomes. Strategies define the actions and initiatives that will help achieve the organization’s goals, while measures provide quantifiable metrics to track progress and success. By carefully selecting and defining strategies and measures for each perspective of the Balanced Scorecard, organizations can ensure that their efforts are aligned with their overall strategy, enabling them to measure and manage performance effectively.
2. Driving Focus and Alignment:
The Balanced Scorecard is not just a measurement tool; it is also a powerful driver of focus and alignment within an organization. By deploying the Balanced Scorecard framework, organizations create a common understanding and language around performance management, which helps align the efforts of employees at all levels. It directs attention to key strategic objectives and ensures that everyone is working towards shared goals. The Balanced Scorecard promotes a culture of discipline and accountability, driving focus and alignment throughout the organization.
3. Performance Indicators:
Performance indicators play a critical role in the Balanced Scorecard framework. They provide organizations with valuable insights into their progress and performance across different perspectives. Performance indicators are specific metrics that organizations track to gauge their performance against targets or benchmarks. These indicators help identify areas of strength and improvement, enabling organizations to take corrective actions and make informed decisions. By carefully selecting and monitoring performance indicators, organizations can effectively measure their progress and adjust their strategies as needed.
Having a clear understanding of strategies, measures, and performance indicators is essential for organizations to harness the power of the Balanced Scorecard. These resources enable organizations to identify key focus areas, align their efforts, and effectively monitor performance. By utilizing the Balanced Scorecard framework in conjunction with these resources, organizations can enhance their decision-making processes, improve operational performance, and achieve their strategic goals.
Balanced Scorecard Basics
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic planning and management system that provides organizations with a comprehensive framework for measuring and improving their performance. It goes beyond traditional approaches that focus solely on financial indicators and encompasses a broader set of perspectives to achieve strategic alignment and long-term success.
Strategic Planning and Management System:
At its core, the Balanced Scorecard serves as a strategic planning and management system that helps organizations translate their vision, mission, and strategy into tangible objectives and action plans. By incorporating multiple perspectives such as financial, customer, process, and learning and growth, the Balanced Scorecard enables organizations to assess performance in a more holistic manner. It emphasizes the importance of aligning key activities and measures with strategic priorities to drive organizational success.
Utilization in Various Sectors:
The versatility of the Balanced Scorecard makes it applicable to various sectors and industries. It has been successfully adopted across organizations of different sizes, including both profit-oriented businesses and non-profit entities. Whether in manufacturing, services, healthcare, government, or education, the Balanced Scorecard has proven to be a valuable tool for improving organizational performance and driving strategic outcomes.
In the private sector, businesses have utilized the Balanced Scorecard to align operational activities with strategic goals, enhance customer satisfaction, optimize internal processes, and support employee learning and growth. Non-profit organizations have found value in using the Balanced Scorecard to measure the achievement of their mission and communicate their impact to stakeholders. Government agencies have also embraced the Balanced Scorecard to improve service delivery, enhance transparency, and align their operations with strategic objectives.
The Balanced Scorecard’s wide-ranging applicability highlights its flexibility and adaptability to the unique needs and contexts of different sectors. Its ability to provide a balanced view of organizational performance ensures that organizations can effectively navigate complex business environments and make informed decisions based on a more comprehensive set of metrics.
By utilizing the Balanced Scorecard as a strategic planning and management system, organizations are better positioned to clarify objectives, align activities, measure outcomes, and drive continuous improvement. It serves as a guiding framework that helps organizations stay focused on their strategic priorities while achieving a balanced and well-rounded approach to success.
Strategy Mapping and Performance Measures
Strategy mapping and performance measures are integral components of the Balanced Scorecard framework, enabling organizations to effectively translate strategy into action and monitor progress towards strategic objectives. They play a crucial role in aligning activities, tracking performance, and facilitating meaningful decision-making.
Strategy Map Importance:
A strategy map is a visual representation that illustrates how an organization’s strategic objectives are interconnected across the four perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard. It depicts the cause-and-effect relationships between different objectives, showcasing how success in one perspective influences outcomes in other perspectives. Strategy maps provide a clear and concise overview of the organization’s strategic goals and the pathways by which they are achieved. They help communicate the strategy to employees, align efforts, and foster a shared understanding of how individual contributions contribute to the organization’s overall success.
Performance Measures and KPIs:
Performance measures and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are critical tools for assessing progress and success in achieving strategic objectives. They provide quantifiable metrics that enable organizations to monitor performance, identify strengths and weaknesses, and drive improvement. Performance measures should align with the strategic objectives and reflect the desired outcomes within each perspective of the Balanced Scorecard. KPIs are selected based on their relevance, reliability, measurability, and ability to provide meaningful insights into performance. Well-defined performance measures and KPIs enable organizations to track progress, make data-driven decisions, and take corrective actions to stay on course towards strategic success.
Performance measures and KPIs should be carefully chosen to ensure they drive desired behaviors, align with the organization’s strategy, and focus on what matters most for achieving objectives. They enable organizations to accurately gauge performance, understand areas requiring attention, and foster a performance-driven culture. Regularly tracking and reviewing performance measures and KPIs provides organizations with timely information to identify trends, diagnose performance gaps, and formulate targeted improvement initiatives.
By employing strategy mapping to visualize the connections between strategic objectives and selecting appropriate performance measures and KPIs, organizations can effectively monitor progress, communicate objectives, and make strategic decisions based on reliable data. These tools strengthen the effectiveness of the Balanced Scorecard by bridging the gap between strategy and execution, providing a clear roadmap for success, and ensuring organizational efforts are aligned to achieve desired outcomes.
Strategic Initiatives and Cascading
Strategic initiatives and cascading are crucial elements of the Balanced Scorecard framework, ensuring that the organization’s strategic objectives are translated into actionable plans at all levels of the organization. They help align individual contributions and initiatives with the overall strategy, fostering a cohesive and coordinated approach towards achieving strategic goals.
Definition and Importance:
Strategic initiatives refer to specific projects, programs, or actions undertaken by an organization to realize its strategic objectives. These initiatives are designed to address strategic priorities, drive change, and improve performance in line with the organization’s overall strategy. They provide a roadmap for implementing the necessary activities and allocating resources effectively to achieve desired outcomes.
Cascading refers to the process of aligning strategic objectives, initiatives, and measures from the top level of the organization down to individual teams and employees. It involves breaking down strategic objectives into actionable tasks and ensuring that each level understands its role in contributing towards the overall strategy. Cascading helps create a clear line of sight between individual performance and the achievement of organizational goals.
Cascading and Alignment:
Cascading ensures that the organization’s strategy is effectively communicated, understood, and executed at all levels. It enables alignment between different levels of the organization, ensuring that the efforts of individuals, teams, and departments are coordinated and focused towards shared objectives.
Cascading begins with translating high-level strategic objectives into actionable initiatives and performance measures at each organizational level. This involves identifying the specific actions, resources, and timelines required to achieve the strategic objectives. As the objectives cascade down through the organization, they are customized and aligned with the roles and responsibilities of different teams, managers, and employees.
Alignment is essential for achieving strategic objectives, as it helps avoid silos and conflicting priorities. By aligning initiatives and goals across different levels of the organization, organizations enhance collaboration, promote accountability, and maximize the collective impact of individual efforts towards overall success.
Strategic initiatives and cascading enable organizations to bridge the gap between strategy formulation and execution. They ensure that the organization’s strategy is translated into tangible actions, instilling a sense of purpose and direction throughout the organization. By aligning strategic initiatives and cascading objectives, organizations optimize their chances of successfully achieving their strategic goals and driving performance improvement.
Automation and Performance Analysis

Automation and performance analysis are essential aspects of the Balanced Scorecard framework. They involve leveraging technology and performance management software to streamline data collection, analysis, and reporting processes. These tools aid in effective decision-making, facilitate continuous improvement, and enhance the overall performance management process.
Utilizing Performance Management Software:
Performance management software plays a crucial role in the implementation of the Balanced Scorecard. It enables organizations to collect, track, and analyze performance data efficiently. Performance management software provides a centralized platform for capturing key performance indicators (KPIs), monitoring progress, and generating insightful reports. By automating data collection and analysis, organizations can save time and resources, reduce manual errors, and gain real-time visibility into performance. This enables managers to make informed decisions based on accurate and timely information.
Performance management software also facilitates collaboration and communication by providing a centralized platform for sharing performance data and reports across different levels and functions within the organization. It promotes transparency and accountability, ensuring that the right stakeholders have access to relevant performance information.
By leveraging performance management software, organizations can streamline their performance analysis efforts, gain actionable insights from performance data, and make informed decisions to achieve their strategic objectives. Automation and performance analysis tools are critical for optimizing the Balanced Scorecard process and ensuring that organizations can effectively monitor and improve their performance.
Usage and Importance of Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard holds significant importance in modern organizational management, supporting strategic decision-making, performance tracking, and alignment of activities with strategic goals. Its usage and implementation signify its pivotal role in organizational success.
Enrol in: Business Process Automation Certification Course
Importance and Strategic Value:
The Balanced Scorecard is vital for organizations due to its ability to align strategic objectives with operational activities. It provides a unified framework that enables organizations to measure and manage performance across multiple dimensions, including financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth perspectives. This comprehensive approach ensures that organizations can evaluate their performance holistically, leading to informed decision-making and strategic planning that reflects a balanced set of priorities.
The strategic value of the Balanced Scorecard is evident in its role in translating an organization’s vision and strategy into practical and measurable objectives. It promotes a clear understanding of strategic priorities among employees at all levels, fostering alignment, motivation, and accountability. By offering a balanced view of performance, the Balanced Scorecard helps organizations adapt to changing conditions, identify areas for improvement, and strive for long-term sustainability and success.
Implementation Process:
The implementation process of the Balanced Scorecard involves defining strategic objectives, selecting performance measures, aligning initiatives, and cascading objectives throughout the organization. This process begins with a clear articulation of the organization’s vision and strategy, followed by the identification of key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect strategic priorities. Initiatives are then developed to support the achievement of these objectives, and the objectives are cascaded down to different organizational levels, ensuring alignment with individual roles and responsibilities.
Successful implementation of the Balanced Scorecard requires commitment from leadership, effective communication, and a continuous improvement mindset. It involves ongoing monitoring, periodic reviews, and the flexibility to adapt to changing circumstances. The implementation process aims to embed the Balanced Scorecard as a central component of the organization’s management practices, guiding day-to-day operations and long-term planning.
Common Uses:
The Balanced Scorecard is commonly used to monitor and evaluate organizational performance, support strategic planning, and guide resource allocation. It serves as a basis for setting and communicating performance expectations, facilitating meaningful discussions around performance, and driving initiatives that align with strategic objectives. It is also frequently utilized in guiding performance-based compensation systems, fostering a culture of accountability and performance improvement.
In summary, the Balanced Scorecard is important due to its ability to align strategic objectives, promote a balanced view of organizational performance, and support informed decision-making. Its implementation process ensures that organizations can effectively execute their strategy and adapt to changing conditions, making it a valuable tool for driving organizational success and sustainable growth.