Table of Contents
Introduction
In the world of project management, uncertainty is often a constant companion. Projects can shift due to unexpected changes in scope, resources, or market conditions. Traditional methods, like the waterfall approach, often require detailed planning upfront, leaving little room for adjustments. This rigidity can lead to frustration when plans inevitably change.
Enter rolling wave planning—a dynamic approach that allows project managers to adapt to changes while keeping the project on track. Rolling wave planning emphasizes iterative processes, enabling teams to plan in stages rather than all at once. This method encourages continuous assessment and adjustment, ensuring that project goals remain achievable even in the face of uncertainty.
In this blog, we will explore what rolling wave planning is, why it matters, and how it can be a game-changer for managing complex projects. Whether you’re a seasoned project manager or new to the field, understanding rolling wave planning can help you navigate the challenges of modern project management with confidence.
Understanding Rolling Wave Planning
Rolling wave planning is a project management technique that involves planning in stages, focusing on immediate tasks while allowing for flexibility in future planning. Unlike traditional approaches that require a comprehensive project plan upfront, rolling wave planning recognizes that not all project details are known at the start.
At its core, rolling wave planning encourages teams to break down projects into manageable parts or “waves.” Each wave represents a defined period where specific tasks are planned, executed, and evaluated. As the project progresses, more details emerge, allowing project managers to refine subsequent waves.
This technique is particularly useful in complex projects where uncertainties are high, such as software development or research and development (R&D) initiatives. By focusing on short-term objectives, teams can respond quickly to changes and adapt their plans based on real-time information.
For example, in a software development project, the team might plan the first wave to include initial features, allowing room for adjustments based on user feedback before planning the next set of features. This iterative approach helps ensure that the project remains aligned with stakeholder expectations and market needs.
The Rationale Behind Rolling Wave Planning
Rolling wave planning addresses some of the key challenges faced in traditional project management methods. One major limitation of the waterfall approach is its reliance on detailed planning from the outset, which can lead to issues if circumstances change. For instance, if a project requires a significant shift in direction, teams may find themselves stuck with a plan that no longer serves their goals.
In today’s fast-paced environment, projects often involve a degree of uncertainty. Market dynamics, evolving customer needs, and technological advancements can all impact project outcomes. Rolling wave planning recognizes this reality and provides a framework that allows for flexibility.
By allowing project managers to adapt their plans based on new information, rolling wave planning fosters a proactive approach to managing risks. Instead of being rigidly bound to an initial plan, teams can pivot when necessary, ensuring that they remain on track to meet their objectives.
Furthermore, this approach encourages collaboration among team members. Frequent check-ins and updates promote communication, ensuring that everyone is aligned and aware of any changes in project scope or direction. Ultimately, rolling wave planning empowers teams to navigate uncertainty with confidence, increasing the likelihood of project success.
Key Benefits of Rolling Wave Planning
Rolling wave planning offers several key benefits that can significantly enhance project management effectiveness:
- Agility: One of the standout advantages of rolling wave planning is its agility. Projects rarely proceed exactly as planned, and this technique allows teams to adjust quickly in response to changes. This responsiveness is crucial in environments where market conditions or client needs can shift unexpectedly.
- Risk Management: By focusing on short-term objectives, rolling wave planning facilitates better risk management. Project managers can identify potential risks early in the process and make informed decisions to mitigate them. This proactive approach reduces the chances of encountering major issues later in the project.
- Enhanced Team Collaboration: Rolling wave planning encourages open communication among team members. Regular updates and reviews ensure that everyone is on the same page, promoting a collaborative environment. This increased interaction helps team members feel more engaged and accountable for their work.
- Improved Clarity: With rolling wave planning, project managers provide clarity on immediate tasks while leaving room for future planning. Team members understand their short-term goals, which helps maintain focus and motivation. As details become clearer, they can anticipate what lies ahead, reducing uncertainty and anxiety.
- Better Stakeholder Engagement: Frequent progress updates help keep stakeholders informed and engaged throughout the project. This transparency builds trust and ensures that stakeholders are aligned with project developments, which can lead to stronger support and satisfaction.
In summary, rolling wave planning not only increases the likelihood of project success but also creates a more dynamic and collaborative project environment. By leveraging these benefits, project managers can lead their teams through uncertainty with confidence and clarity.
Industries and Projects That Thrive with Rolling Wave Planning
Rolling wave planning is particularly well-suited for industries and projects characterized by uncertainty, complexity, and the need for innovation. Here are some key sectors where this approach shines:
- Software Development: The tech industry often faces rapid changes in user requirements and market dynamics. Rolling wave planning allows software development teams to focus on delivering initial features while gathering user feedback to refine future iterations. This ensures that the final product aligns with user needs and expectations.
- Research and Development (R&D): In R&D projects, the end goal is often not clearly defined at the outset. These projects typically involve exploration and experimentation, making rolling wave planning an ideal fit. As new findings emerge, project teams can adjust their plans, ensuring that they remain aligned with evolving goals.
- Construction Projects: In construction, factors like weather, material availability, and regulatory changes can affect timelines and costs. Rolling wave planning allows project managers to develop detailed plans for initial phases while maintaining flexibility to adapt to unforeseen challenges in later phases.
- Marketing Campaigns: In fast-paced marketing environments, strategies often need to shift based on real-time data and audience feedback. Rolling wave planning enables marketing teams to launch campaigns in stages, allowing for adjustments based on initial performance metrics.
By applying rolling wave planning across these diverse industries, organizations can effectively manage uncertainty while fostering innovation and responsiveness to change.
Rolling Wave Planning vs. Other Methodologies
While rolling wave planning shares some similarities with other project management methodologies, it also has distinct characteristics that set it apart. Understanding these differences can help project managers select the most suitable approach for their projects.
- Agile Sprints: Rolling wave planning and agile sprints are both iterative methods that promote flexibility. However, agile sprints focus on delivering a set of features within a defined timeframe, often with less emphasis on sequential tasks. In contrast, rolling wave planning maintains a clear sequence of tasks with firm deadlines, making it more suitable for projects with structured timelines.
- Waterfall Method: The traditional waterfall method relies on comprehensive upfront planning and a linear sequence of phases. Once the project begins, changes to the plan can be difficult and costly to implement. Rolling wave planning, on the other hand, embraces change by allowing project managers to adapt their plans as new information emerges. This flexibility makes it ideal for projects with uncertain or evolving requirements.
- Critical Path Method (CPM): While both rolling wave planning and CPM focus on scheduling tasks to meet deadlines, rolling wave planning is more dynamic. CPM requires a detailed schedule from the start, whereas rolling wave planning allows for adjustments and updates throughout the project. This adaptability is crucial in environments where project details can change frequently.
By understanding these distinctions, project managers can choose the methodology that best aligns with their project goals and environments, ensuring a higher likelihood of success.
Implementing Rolling Wave Planning: A Step-by-Step Guide
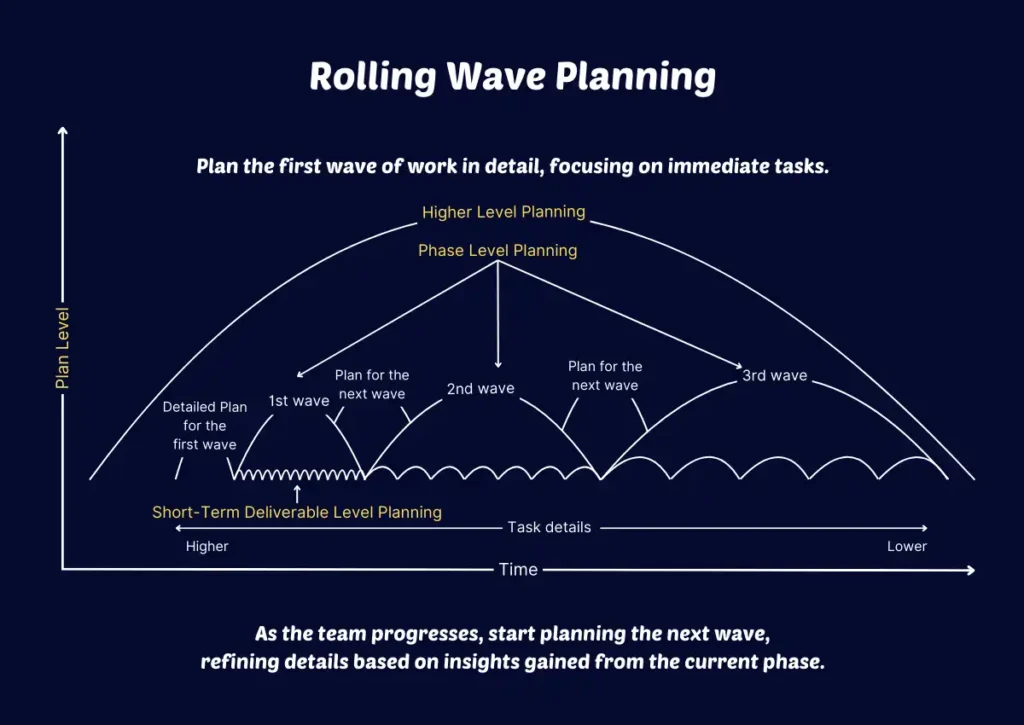
Implementing rolling wave planning involves a structured approach that allows project managers to maintain flexibility while ensuring progress. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
- Identifying Risks and Setting Initial Goals: Begin by conducting a risk assessment to identify potential challenges that could impact your project. Engage your team in discussions about project goals, deliverables, and deadlines. Clearly outline roles and responsibilities to ensure everyone understands their contributions.
- Creating the First Planning Horizon: Develop a timeline and budget for the initial phase of the project, also known as the first planning horizon. Utilize a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to define tasks and deliverables, breaking the overall project into smaller, manageable components. This helps create clarity and sets the foundation for the next steps.
- Defining Waves and Iterations: Plan the first wave of work in detail, focusing on immediate tasks. This wave should include specific objectives, timelines, and resources needed. As the team progresses, start planning the next wave, refining details based on insights gained from the current phase.
- Establishing a Baseline for Measurement: Create a baseline for project scope, cost, and schedule. This baseline serves as a reference point for measuring progress and assessing whether the project is on track. Regularly review this baseline to identify any variances that may require adjustments.
- Executing and Monitoring Progress: Launch the first wave and ensure that team members are actively working on their assigned tasks. Monitor progress closely, providing support and guidance as needed. Regular check-ins and updates will help keep the team aligned and focused on objectives.
- Iterating Until Project Completion: Continue the process of planning and executing subsequent waves until the project is completed. After each wave, conduct a review to assess what worked well and what didn’t. This reflection helps improve future iterations and enhances overall project management skills.
By following these steps, project managers can successfully implement rolling wave planning, leading to increased adaptability and project success.
Real-World Applications and Success Stories
Rolling wave planning has proven to be a valuable approach in various industries, leading to successful project outcomes. Here are a few real-world examples that illustrate its effectiveness:
- Software Development at a Tech Startup: A tech startup utilized rolling wave planning to develop a new mobile app. By focusing on the first wave, which included core features, the team was able to launch a minimum viable product (MVP) quickly. User feedback from the MVP informed subsequent waves, allowing the team to enhance features and address user needs effectively. This iterative approach resulted in a highly successful app launch and satisfied customers.
- Research and Development in Pharmaceuticals: A pharmaceutical company applied rolling wave planning to manage its R&D projects for new drug development. As initial phases provided insights into compound efficacy, the project team adapted their strategies based on emerging data. This flexibility enabled them to make informed decisions and optimize the research process, ultimately leading to a faster time-to-market for a groundbreaking new medication.
- Construction Project Adaptation: In a large construction project, the project manager faced unexpected delays due to weather conditions. By implementing rolling wave planning, the team was able to adjust their work schedules, focusing on areas unaffected by the weather. This adaptability allowed the project to stay on track despite external challenges, demonstrating how rolling wave planning can effectively manage real-world uncertainties.
These success stories highlight the power of rolling wave planning in various contexts, showcasing its ability to enhance project management outcomes through flexibility, adaptability, and collaboration.
Tools and Techniques to Facilitate Rolling Wave Planning
Implementing rolling wave planning effectively requires the right tools and techniques to streamline processes and enhance collaboration among team members. Here are some recommended tools that can support rolling wave planning:
- Project Management Software: Tools like Asana, Trello, and Jira offer features that facilitate rolling wave planning, including task management, timelines, and collaboration functionalities. These platforms allow teams to break projects into waves, assign tasks, and track progress in real-time, making it easier to adjust plans as needed.
- Gantt Charts: Gantt charts are a visual representation of project timelines that can be particularly useful in rolling wave planning. They help project managers map out phases, tasks, and deadlines clearly. Software like Microsoft Project or Smartsheet allows for dynamic adjustments, enabling managers to shift tasks and timelines based on current project realities.
- Dashboards and Reporting Tools: Utilizing dashboards provides project managers with a high-level overview of project progress. Tools like Tableau or built-in reporting features in project management software help visualize key metrics, identify bottlenecks, and make data-driven decisions quickly.
- Collaboration Platforms: Communication is crucial in rolling wave planning. Tools such as Slack or Microsoft Teams enhance team collaboration by facilitating discussions, file sharing, and updates in real time. This ensures that team members remain aligned on objectives and changes.
By leveraging these tools and techniques, project managers can enhance their rolling wave planning process, enabling them to navigate complexities and uncertainties more effectively.
Conclusion
In today’s fast-paced and ever-changing project landscape, rolling wave planning emerges as a vital approach for managing uncertainty and complexity. By allowing teams to plan iteratively and adapt to new information, this method not only fosters agility but also encourages collaboration and innovation.
The benefits of rolling wave planning—such as improved risk management, enhanced clarity, and stronger stakeholder engagement—make it a powerful tool for project managers across various industries. From software development to research and construction, the flexibility of rolling wave planning enables teams to respond effectively to evolving project dynamics.
As you consider integrating rolling wave planning into your project management practices, reflect on your current methodologies. Are they flexible enough to adapt to change? By embracing the principles of rolling wave planning, you can navigate the uncertainties of project management with confidence and lead your team to successful outcomes.











